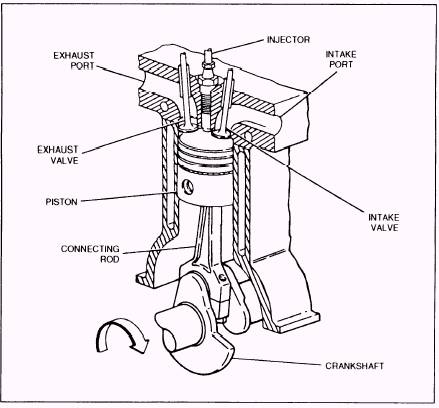
Four-stroke engine

Four-stroke cycle used in gasoline/petrol engines. The right blue
side is the intake and the left brown side is the exhaust. The cylinder
wall is a thin sleeve surrounded by cooling liquid.A four-stroke engine,
also known as four-cycle, is an internal combustion engine in which the
piston completes four separate strokes—intake, compression, power, and
exhaust—during two separate revolutions of the engine’s crankshaft, and
one single thermodynamic cycle.
There are two common types of engines, which are closely related to
each other but have major differences in their design and behavior. The
earliest of these to be developed is the Otto cycle engine which was
developed in 1876 by Nikolaus August Otto in Cologne, Germany, after the
operation principle described by Alphonse Beau de Rochas in 1861. This
engine is most often referred to as a petrol engine or gasoline engine,
after the fuel that powers it. The second type of four-cycle engine is
the Diesel engine developed in 1893 by Rudolph Diesel, also of Germany.
Diesel created his engine to maximize efficiency which was lacking in
the Otto engine. There are several major differences between the Otto
cycle engine and the four-cycle diesel engine. The diesel engine is made
in both a two-cycle and a four-cycle version. Ironically Otto’s company
Deutz AG produces primarily diesel engines in the modern era.
The Otto cycle is named after the 1876 engine of Nikolaus A. Otto,
who built a successful four-cycle engine which was based on the work of
Jean Joseph Etienne Lenoir. It was the third engine type that Otto
developed. It used a sliding flame gateway for ignition of its fuel
which was a mixture of illuminating gas and air. After 1884 Otto also
developed the magneto allowing the use of an electrical spark for ignition, which had been unreliable on the Lenoir engine.
The internal combustion engine (ICE) is used in motorcycles,
automobiles, boats, trucks, aircraft, ships, heavy duty machinery, and
in its original intended use as stationary power both for kinetic and electrical
power generation. Diesel engines are found in virtually all heavy duty
applications such as trucks, ships, locomotives, power generation, and
stationary power. Many of these diesel engine are two-cycle with power
ratings up to 105,000 hp (78,000 kW).
The four cycles refer to suction(intake), compression, combustion
(power), and exhaust cycles that occur during two crankshaft rotations
per power cycle of the four-cycle engines. The cycle begins at Top Dead
Centre (TDC), when the piston is farthest away from the axis of the
crankshaft. A cycle refers to the full travel of the piston from Top
Dead Centre (TDC) to Bottom Dead Centre (BDC).
Many of us may know about two stroke or four stroke engine.Those who
are from mechanical or automobile field must have to familiar with this
term.Actually two stroke or four stroke is the cycle of any
reciprocating engine.When only two stroke required to complete the
reciprocating engine cycle then that engine is known as two stroke
engine,and when four stroke required to complete the cycle then it is
known as four stroke engine.
In four stroke engine the work is obtained only during one stroke out
of these for a single cylinder engine or for every cylinder
individually for multi cylinder engine.If you have any automobile
vehicle or machine,then you better know the above terms.
This is first stroke of your engine.During this stroke the piston is
moved downward from Top Dead Centre by means of crankshaft which is
rotate by electric
motor.This movement increases the size of combustion space thereby
reducing the pressure inside the cylinder,as the result,the higher
pressure of the outside atmosphere forces the air into combustion space
through suction valve.The exhaust valve remain closed in this stroke.
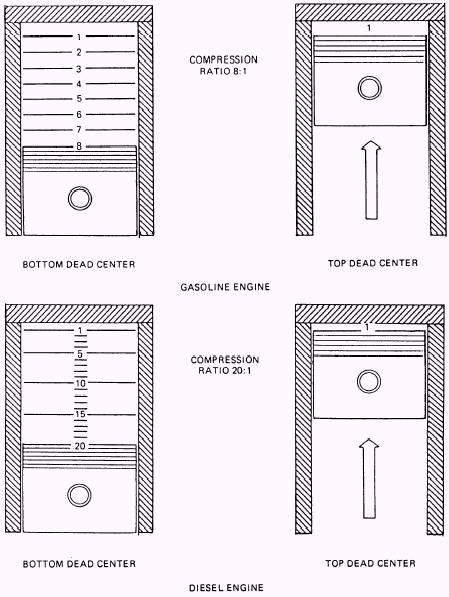
2)Compression Stroke.
This is second stroke of your engine.The air-fuel mixture is
compressed during this upward stroke.The compression,forces the fuel
into closer combination with air.Heat is produced due to compression
aids the combustion of fuel.Just a little before the end of compression
stroke the mixture is ignited by a spark produced by spark plug.During
this stroke suction and exhaust valve remain closed.
3)Power Stroke.
This is third stroke of your engine.You may call it as Expansion
Stroke also.The air-fuel mixture which burns at the end of compression
stroke expands due to heat of combustion.This expansion of burnt
air-fuel mixture exerts pressure in the cylinder and on the piston,and
under this impulse the piston moves downward thus doing useful
work.Suction and exhaust valve remain closed during this stroke.
4)Exhaust Stroke.
This is last stroke of your engine.During this stroke the suction
valve remain closed while the exhaust valve opens.The greater part of
burnt gases escape because of their own expansion.The upward movement of
piston pushes the remaining gases out of the open exhaust valve.Thus
complete the exhaust stroke and one cycle of engine.
stroke engine.
No comments:
Post a Comment